ABC Model#
A simple model coupling biosphere and atmosphere made fully differentiable using JAX built up on the CLASS model.
Installation#
These instructions work on Linux and MacOS and assume that python with pip is installed already. Otherwise, install python and pip with the tool of your choice, such as miniforge or uv, before you proceed. See below for full instructions to install on Windows.
Install with
pip install git@github.com/EarthyScience/abc-model
or clone the repo and make an editable install inside your local repo using
pip install -e .
If you want to use jax on GPUs, change the tag from [cpu] to [gpu] in an environment with GPUs installed.
This is not necessary to run the examples in this repository.
Quick example#
To setup the coupler we will always use 3 components:
Radiation model (rad)
Land surface model (land)
Atmosphere model (atmos)
The atmosphere model uses 3 components:
3.1. Surface layer model
3.2. Mixed layer model
3.3. Cloud model
Each model is a class that is initialized with model-specific parameters. We provide a config example (which we take from the CLASS model).
This can be loaded through the abcconfigs module:
import abcconfigs.class_model as cm
Now we are ready to set up our models with ease…
We will do this using the abcmodel module, which is the de facto module in this repository.
import abcmodel
# setup models
rad_model = abcmodel.rad.StandardRadiationModel(**cm.standard_rad.model_kwargs)
land_model = abcmodel.land.JarvisStewartModel(**cm.jarvis_stewart.model_kwargs)
surface_layer_model = abcmodel.atmos.surface_layer.ObukhovSurfaceLayerModel()
mixed_layer_model = abcmodel.atmos.mixed_layer.BulkMixedLayerModel(**cm.bulk_mixed_layer.model_kwargs)
cloud_model = abcmodel.atmos.clouds.CumulusModel()
# setup atmos model
atmos_model = abcmodel.atmos.DayOnlyAtmosphereModel(
surface_layer=surface_layer_model,
mixed_layer=mixed_layer_model,
clouds=cloud_model,
)
# setup coupler
abcoupler = abcmodel.ABCoupler(
rad=rad_model,
land=land_model,
atmos=atmos_model,
)
# setup initial conditions for each model
rad_state = rad_model.init_state(**cm.standard_rad.state_kwargs)
land_state = land_model.init_state(**cm.jarvis_stewart.state_kwargs)
surface_layer_state = surface_layer_model.init_state(**cm.obukhov_surface_layer.state_kwargs)
mixed_layer_state = mixed_layer_model.init_state(**cm.bulk_mixed_layer.state_kwargs)
cloud_state = cloud_model.init_state()
# setup atmos state
atmos_state = atmos_model.init_state(
surface=surface_layer_state,
mixed=mixed_layer_state,
clouds=cloud_state,
)
# finally we can use the coupler to bound everything in a initial state
state = abcoupler.init_state(
rad_state,
land_state,
atmos_state,
)
All set - let’s integrate our model by defining the timestepping and the run time.
# time step [s]
inner_dt = 15.0 # this is the "running" time step
outter_dt = 60.0 * 30 # this is the "diagnostic" time step
# total run time [s]
runtime = 12 * 3600.0
# start time of the day [h]
tstart = 6.5
time, trajectory = abcmodel.integrate(
state, abcoupler, inner_dt, outter_dt, runtime, tstart
)
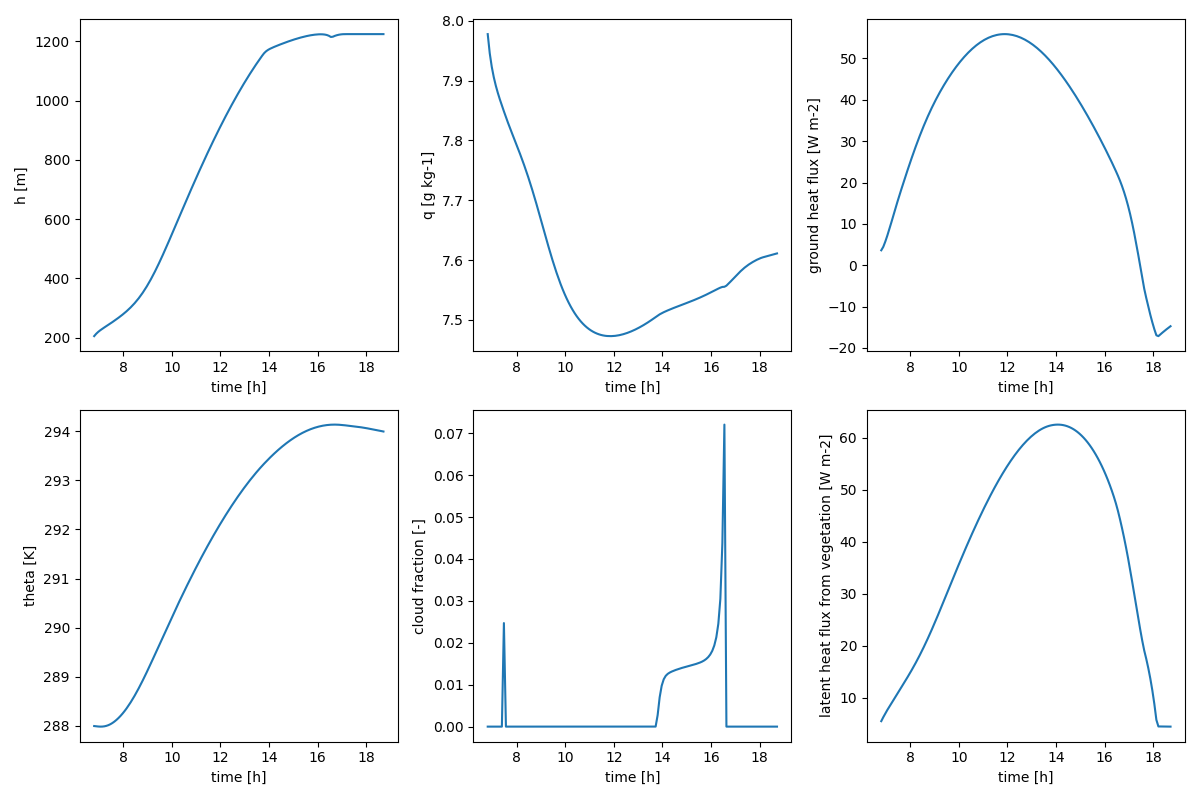
To plot the results, we will typically follow something like the code below.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# plot output
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
plt.subplot(231)
plt.plot(time, trajectory.atmos.mixed.h_abl)
plt.xlabel("time [h]")
plt.ylabel("h [m]")
plt.subplot(234)
plt.plot(time, trajectory.atmos.mixed.theta)
plt.xlabel("time [h]")
plt.ylabel("theta [K]")
plt.subplot(232)
plt.plot(time, trajectory.atmos.mixed.q * 1000.0)
plt.xlabel("time [h]")
plt.ylabel("q [g kg-1]")
plt.subplot(235)
plt.plot(time, trajectory.atmos.clouds.cc_frac)
plt.xlabel("time [h]")
plt.ylabel("cloud fraction [-]")
plt.subplot(233)
plt.plot(time, trajectory.land.gf)
plt.xlabel("time [h]")
plt.ylabel("ground heat flux [W m-2]")
plt.subplot(236)
plt.plot(time, trajectory.land.le_veg)
plt.xlabel("time [h]")
plt.ylabel("latent heat flux from vegetation [W m-2]")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Which should give us something like the figure below.
Documentation#
Detailed documentation of the model is included in the repo. To view the documentation, navigate to docs/_build/html and run
python -m http.server
This will launch a local http server displaying the interactive documentation and print the port to access it in your terminal.
Changing models, parameters and initial conditions#
Now let’s say you want to use a different model for the land surface.
Instead of the Jarvis Stewart model, you may choose Ags.
We also provide a configuration for that, which you can load using the abcconfigs module, as previously done.
You can take a look at the config here.
Now, for example, you may change from C3 to C4 with something like the following.
# new parameters definition
ags_model_kwargs = cm.ags.model_kwargs
ags_model_kwargs['c3c4'] = 'c4'
# define a new land model
land_model = abcmodel.land.AgsModel(**ags_model_kwargs)
Then you can redefine the coupler, create a new state and integrate it to see different outcomes. You can do something similar to change initial conditions, or even recreate your own!
Windows installation#
On Windows we need some more utilities for jax to work properly, also installing python is not as straigforward. For jax to run, you first need the Microsoft Visual C++ redistributable found here, which will require a system restart to function. Note that you might want to install uv before the restart, as the PATH update might require a restart as well (see below).
Now clone the repo and cd into it. The following section shows how to set up a python environment with uv, if you have python with pip running you can skip it.
UV environment#
First install uv via the terminal with
powershell -ExecutionPolicy ByPass -c "irm https://astral.sh/uv/install.ps1 | iex"
You can check that uv is available and running by typing uv in your terminal, if you receive an error, you will have to add uv to your path manually or restart your computer. Here, or when executing uv scripts to activate environments windows execution policiy might stop you, if that is the case you need to change or bypass it.
After uv is installed and running, create a virtual environment in the abc-model directory by running
uv venv --python 3.13.0
this will also show you the command needed to activate the venv, which should look similar to
.venv\Scripts\activate
Lastly, while in the abc-model directory, install the abc-model with uv:
uv pip install -e .
See also#
For a more advanced model, see ClimaLand.jl.