Getting Started
This page demonstrates how to use EasyHybrid to create a hybrid model for ecosystem respiration. You will become familiar with the following concepts:
Key concepts
Process-based Model: The
RbQ10function represents a classical Q10 model for respiration with base respirationrbandQ10which describes the factor by respiration is increased for a 10 K change in temperature.Neural Network: Learns to predict the basal respiration parameter
rbfrom environmental conditions.Hybrid Integration: Combines the neural network predictions with the process-based model to produce final outputs.
Parameter Learning: Some parameters (like
Q10) can be learned globally, while others (likerb) are predicted per sample.
The framework automatically handles the integration between neural networks and mechanistic models, making it easy to leverage both data-driven learning and domain knowledge.
Installation
Install Julia v1.10 or above. EasyHybrid.jl is available through the Julia package manager. You can enter it by pressing ] in the REPL and then typing add EasyHybrid. Alternatively, you can also do
import Pkg
Pkg.add("EasyHybrid")Quickstart
1. Setup and Data Loading
Load package and synthetic dataset
using EasyHybrid
ds = load_timeseries_netcdf("https://github.com/bask0/q10hybrid/raw/master/data/Synthetic4BookChap.nc")
ds = ds[1:20000, :] # Use subset for faster execution
first(ds, 5)| Row | time | sw_pot | dsw_pot | ta | reco | rb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DateTime | Float64? | Float64? | Float64? | Float64? | Float64? | |
| 1 | 2003-01-01T00:15:00 | 109.817 | 115.595 | 2.1 | 0.844741 | 1.42522 |
| 2 | 2003-01-01T00:45:00 | 109.817 | 115.595 | 1.98 | 0.840641 | 1.42522 |
| 3 | 2003-01-01T01:15:00 | 109.817 | 115.595 | 1.89 | 0.837579 | 1.42522 |
| 4 | 2003-01-01T01:45:00 | 109.817 | 115.595 | 2.06 | 0.843372 | 1.42522 |
| 5 | 2003-01-01T02:15:00 | 109.817 | 115.595 | 2.09 | 0.844399 | 1.42522 |
2. Define the Process-based Model
RbQ10 model: Respiration model with Q10 temperature sensitivity
function RbQ10(;ta, Q10, rb, tref = 15.0f0)
reco = rb .* Q10 .^ (0.1f0 .* (ta .- tref))
return (; reco, Q10, rb)
endRbQ10 (generic function with 1 method)3. Configure Model Parameters
Parameter specification: (default, lower_bound, upper_bound)
parameters = (
rb = (3.0f0, 0.0f0, 13.0f0), # Basal respiration [μmol/m²/s]
Q10 = (2.0f0, 1.0f0, 4.0f0), # Temperature sensitivity - describes factor by which respiration is increased for 10 K increase in temperature [-]
)(rb = (3.0f0, 0.0f0, 13.0f0), Q10 = (2.0f0, 1.0f0, 4.0f0))4. Construct the Hybrid Model
Define input variables
forcing = [:ta] # Forcing variables (temperature)
predictors = [:sw_pot, :dsw_pot] # Predictor variables (solar radiation)
target = [:reco] # Target variable (respiration)1-element Vector{Symbol}:
:recoParameter classification as global, neural or fixed (difference between global and neural)
global_param_names = [:Q10] # Global parameters (same for all samples)
neural_param_names = [:rb] # Neural network predicted parameters1-element Vector{Symbol}:
:rbConstruct hybrid model
hybrid_model = constructHybridModel(
predictors, # Input features
forcing, # Forcing variables
target, # Target variables
RbQ10, # Process-based model function
parameters, # Parameter definitions
neural_param_names, # NN-predicted parameters
global_param_names, # Global parameters
hidden_layers = [16, 16], # Neural network architecture
activation = swish, # Activation function
scale_nn_outputs = true, # Scale neural network outputs
input_batchnorm = true # Apply batch normalization to inputs
)Hybrid Model (Single NN)
Neural Network:
Chain(
layer_1 = BatchNorm(2, affine=false, track_stats=true),
layer_2 = Dense(2 => 16, swish), # 48 parameters
layer_3 = Dense(16 => 16, swish), # 272 parameters
layer_4 = Dense(16 => 1), # 17 parameters
) # Total: 337 parameters,
# plus 5 states.
Configuration:
predictors = [:sw_pot, :dsw_pot]
forcing = [:ta]
targets = [:reco]
mechanistic_model = RbQ10
neural_param_names = [:rb]
global_param_names = [:Q10]
fixed_param_names = Symbol[]
scale_nn_outputs = true
start_from_default = true
config = (; hidden_layers = [16, 16], activation = swish, scale_nn_outputs = true, input_batchnorm = true, start_from_default = true,)
Parameters:
Hybrid Parameters
┌─────┬─────────┬───────┬───────┐
│ │ default │ lower │ upper │
├─────┼─────────┼───────┼───────┤
│ rb │ 3.0 │ 0.0 │ 13.0 │
│ Q10 │ 2.0 │ 1.0 │ 4.0 │
└─────┴─────────┴───────┴───────┘5. Train the Model
out = train(
hybrid_model,
ds,
();
nepochs = 100, # Number of training epochs
batchsize = 512, # Batch size for training
opt = RMSProp(0.001), # Optimizer and learning rate
monitor_names = [:rb, :Q10], # Parameters to monitor during training
yscale = identity, # Scaling for outputs
patience = 30, # Early stopping patience
show_progress=false,
) train_history: (101,)
mse (reco, sum)
r2 (reco, sum)
val_history: (101,)
mse (reco, sum)
r2 (reco, sum)
ps_history: (101,)
ϕ ()
monitor (train, val)
train_obs_pred: 16000×3 DataFrame
reco, index, reco_pred
val_obs_pred: 4000×3 DataFrame
reco, index, reco_pred
train_diffs:
Q10 (1,)
rb (16000,)
parameters (rb, Q10)
val_diffs:
Q10 (1,)
rb (4000,)
parameters (rb, Q10)
ps: (338,)
st:
st_nn (layer_1, layer_2, layer_3, layer_4)
fixed ()
best_epoch: 91
best_loss: 0.00450414756. Check Results
Evolution of train and validation loss
using CairoMakie
EasyHybrid.plot_loss(out, yscale = identity)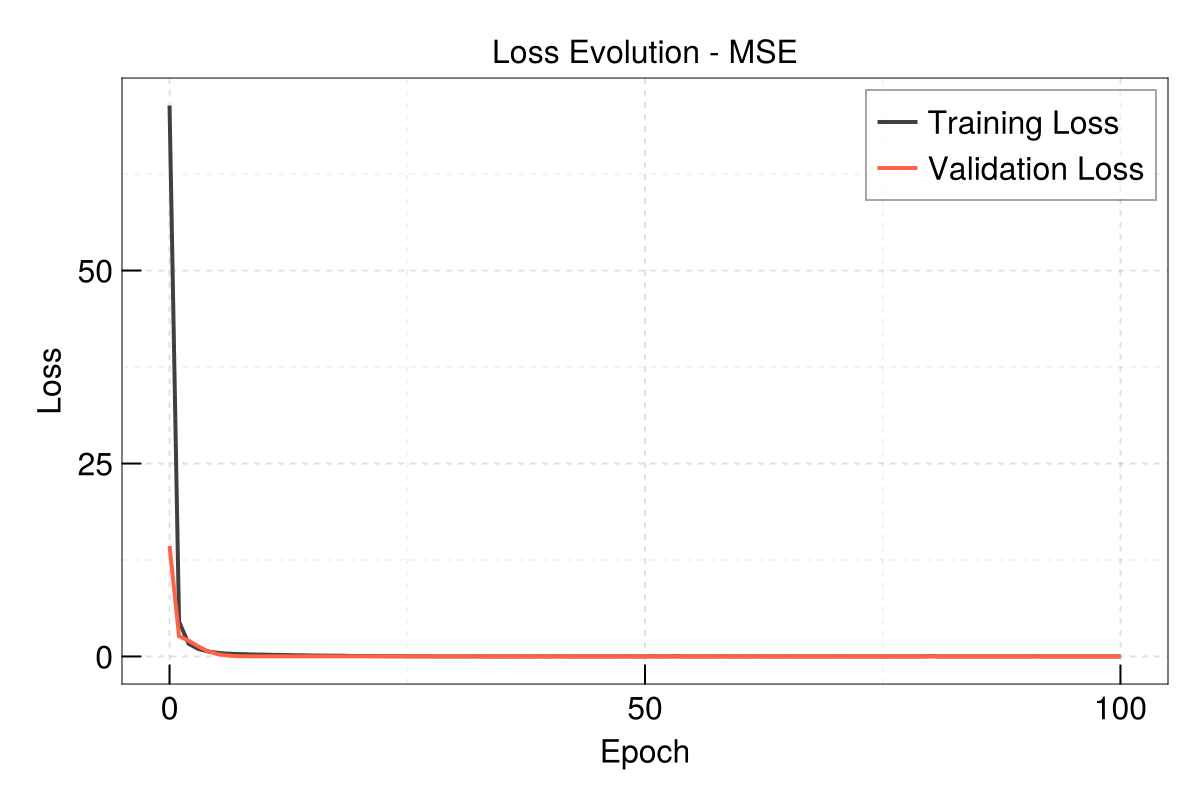
Check results - what do you think - is it the true Q10 used to generate the synthetic dataset?
out.train_diffs.Q101-element Vector{Float32}:
1.4998505Quick scatterplot - dispatches on the output of train
EasyHybrid.poplot(out)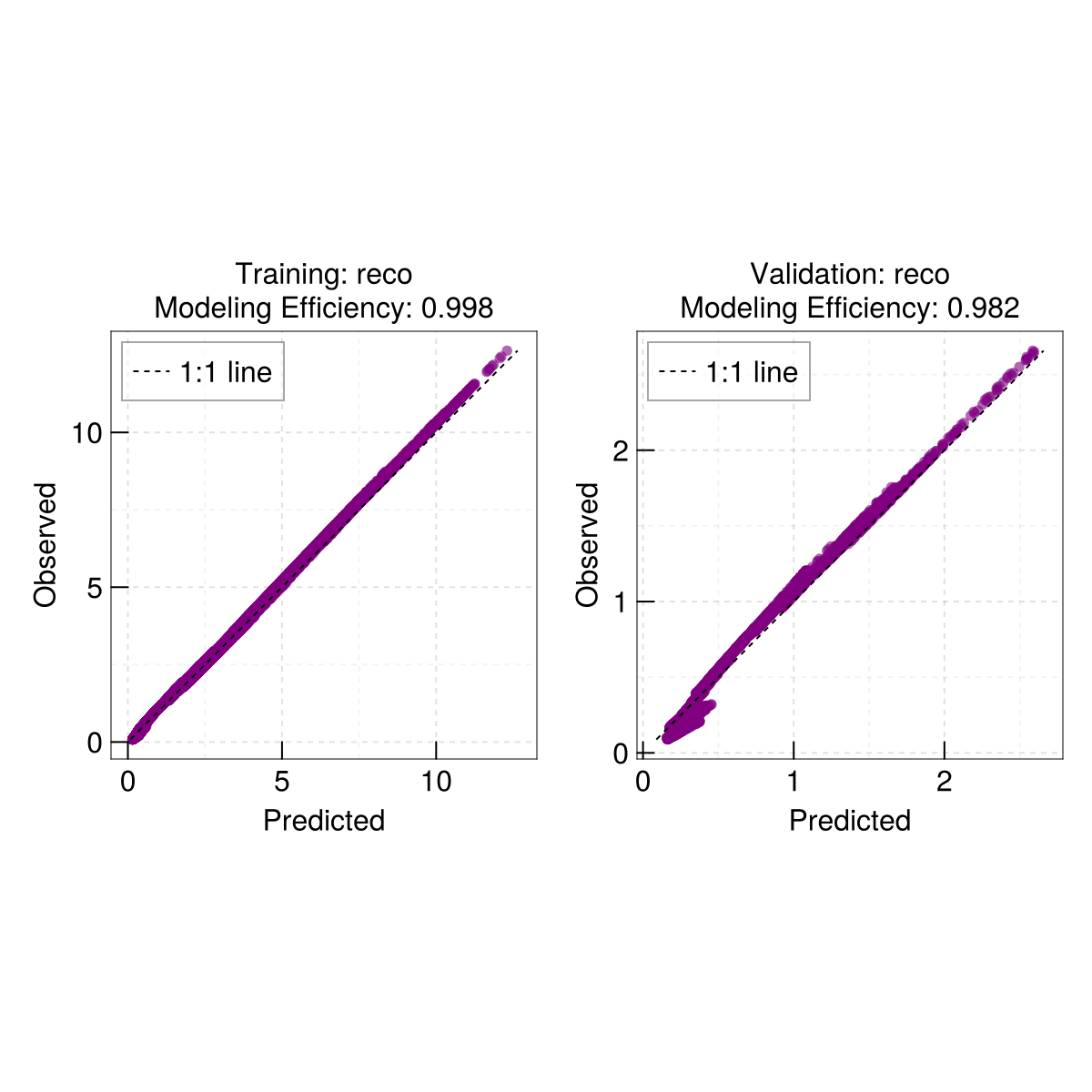
More Examples
Check out the projects/ directory for additional examples and use cases. Each project demonstrates different aspects of hybrid modeling with EasyHybrid.
 Bernhard Ahrens
Bernhard Ahrens